Niacinamide, a form of Vitamin B3, is a popular and highly versatile ingredient found in many skincare products, from face washes to sunscreens. Its widespread use is due to its numerous benefits for various skin concerns. Understanding how to effectively incorporate it into your routine can lead to significant improvements in skin health.
What Niacinamide Does for Your Skin
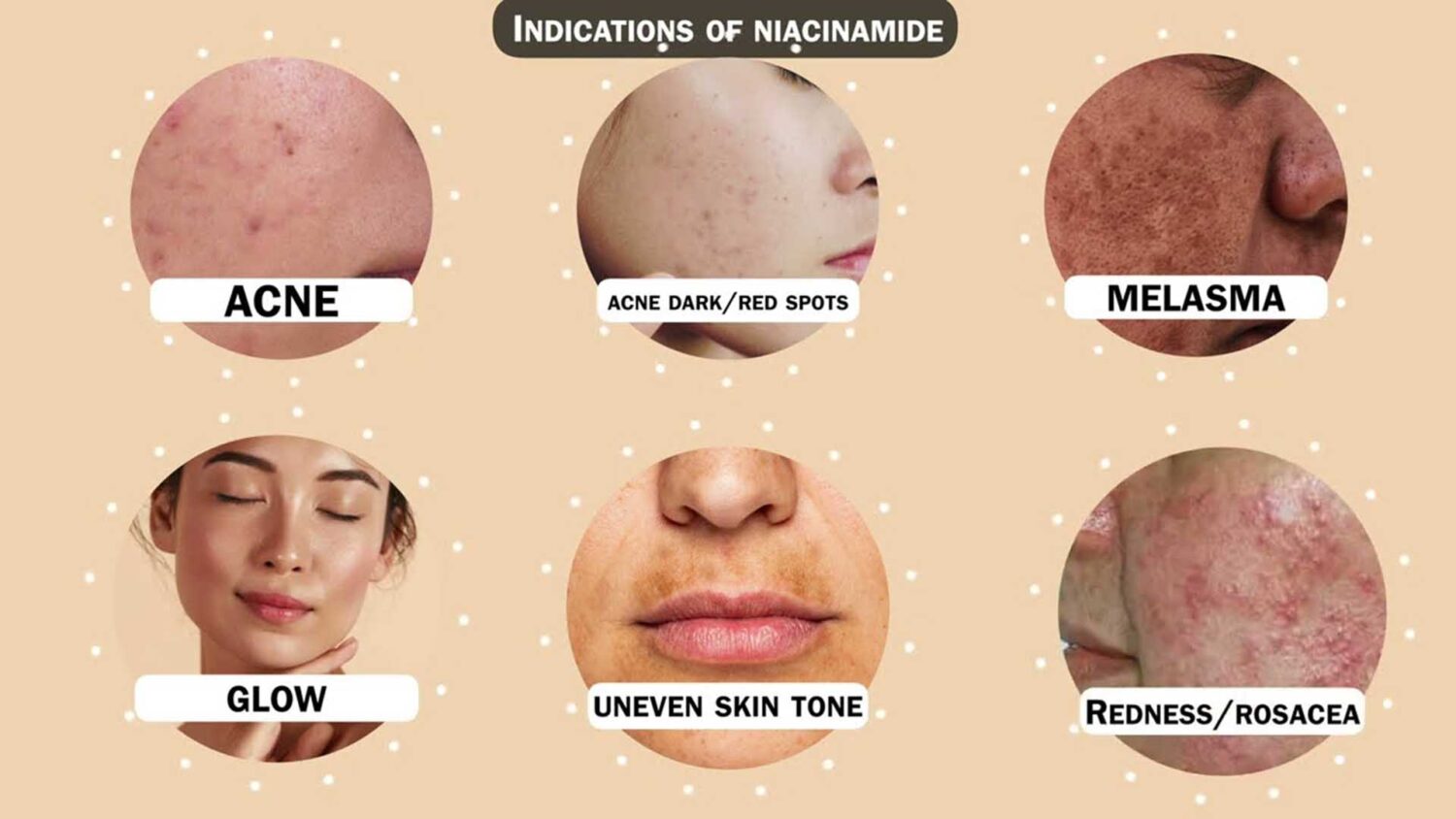
Niacinamide offers a wide array of benefits, making it a valuable addition to most skincare regimens:
- Regulates Oil Production: It helps to reduce oil secretion, making it beneficial for those with oily or acne-prone skin.
- Minimizes Dark Spots: Niacinamide works to lighten dark spots and hyperpigmentation by reducing the transfer of melanin to the skin’s surface.
- Provides Photo-Protection: It offers some protection against sun damage, acting as a supportive element in your sun care routine.
- Reduces Inflammation and Redness: With its anti-inflammatory properties, niacinamide can calm redness and irritation, including conditions like rosacea and red acne marks.
- Strengthens Skin Barrier: By boosting ceramide production, it helps repair the skin’s natural barrier, leading to better hydration and resilience.
- Improves Skin Elasticity and Tone: Some studies suggest it can enhance skin elasticity and even out skin tone, contributing to a smoother, more radiant complexion.
While niacinamide is a powerful ingredient, it generally performs best when combined with other actives, rather than as a standalone treatment for severe concerns.
Who Can Benefit from Niacinamide?
Niacinamide is considered a safe and beneficial ingredient for almost all skin types and ages, particularly:
- Teenagers: Especially those with oily skin or occasional breakouts.
- Sensitive Skin: At a 5% concentration, it can be a gentle yet effective option for easily irritated skin.
- Skincare Beginners: It’s a safe starting point for those new to active ingredients.
- Dry Skin: It helps boost ceramides and repair the skin barrier, reducing dryness.
- Those Undergoing Skin Treatments: It can aid in barrier repair when combined with treatments like peels or lasers (use a 5% concentration).
However, individuals with mature skin (over 40) or severe acne might find more potent ingredients necessary for their primary concerns. Similarly, for stubborn dark spots or melasma, niacinamide is best used in conjunction with other targeted treatments like alpha arbutin or kojic acid, and often prescription-strength creams for melasma.
Choosing and Using Niacinamide
Niacinamide is available in various formulations, but serums and creams offer the most significant benefits. Serums are generally preferred for oily to combination skin, while creams are better suited for dry and sensitive skin types.
- Concentration: A 5% concentration of niacinamide is usually sufficient to see good results. Studies show that using more than 10% can actually increase skin irritation, redness, and itching.
- Formulation Matters: Always consider other ingredients in a niacinamide product. If it contains soothing and hydrating components like Centella asiatica, aloe vera extract, or panthenol, a 10% concentration might be well-tolerated. Otherwise, sticking to 5% is advisable.
- Application:
- Serums: Apply 3-4 drops to a clean, slightly damp face.
- Creams: Apply a thin layer after your serum has absorbed for 2-3 minutes.
- It can be used twice daily.
- Patch Test: For very sensitive skin, always perform a patch test on a small area (like the neck) for 48 hours before applying to the entire face.
- Pursing vs. Irritation: Niacinamide typically does not cause “purging” (an initial breakout of acne due to increased cell turnover). If you experience severe pimples, redness, or irritation, it’s likely an irritation, not purging, and you should discontinue use.
Layering Niacinamide with Other Actives
Niacinamide is known for its compatibility and can be layered effectively with many other skincare ingredients:
- With Vitamin C: Apply Vitamin C first on clean, dry skin, followed by niacinamide serum.
- With Retinoids: For dry skin, apply niacinamide on damp skin, let it absorb, then apply retinoid, and follow with moisturizer. For oily skin, apply retinoid first, then niacinamide.
- With Salicylic Acid: This is an excellent combination for acne-prone and oily skin. Niacinamide can help mitigate the potential dryness and irritation from salicylic acid. Apply niacinamide first, then salicylic acid, either to specific areas (T-zone for combination skin) or the entire face (for oily skin).
- With Glycolic Acid: As glycolic acid (an AHA) can sometimes be irritating, combining it with niacinamide can help reduce skin irritation while still providing benefits for dullness and dark spots.
Discover the Power of Vitamin C Serums for Radiant Skin
Consistent and proper use of niacinamide can significantly improve your skin’s health and appearance. However, remember to always consider your individual skin needs and consult a dermatologist for personalized advice, especially for stubborn concerns like melasma or severe acne.

